
There is also a limit of approx 30,720 files (using MBR) on a single VMFS3 datastore. VMFS5 uses 1 MB blocks throughout (with block suballocation for small files), and has a file size limit of 62 TB, though the VMDK size is restricted to 2 TB - 512 B in ESXi versions earlier than 5.5 due to a limitation in the version of SCSI emulated. VMFS3 limits files to 262,144 (2 18) blocks, which translates to 256 GB for 1 MB block sizes (the default) up to 2 TB for 8 MB block sizes. In vSphere 5.1, this limit is increased to 32 with the introduction of a new locking mechanism. 
This affects the scalability of linked clones sharing the same base image.
In VMFS3 and VMFS5 prior to vSphere 5.1, the maximum number of hosts which can share a read-only file is 8. Maximum LUN size of 2 TB as of VMFS3 and 64 TB as of VMFS5. Maximum filesystem size is 50 TB as of VMFS3, and 62 TB as of VMFS5. Can be shared with up to 64 ESXi Servers. While present in previous versions automatic unmap was added to VMFS 6 allowing for automatic space reclamation requests which previously were manually actioned. Recover virtual machines faster and more reliably in the event of server failure with Distributed Journaling. Optimize virtual machine I/O with adjustable volume, disk, file and block sizes. With ESX/ESXi4, VMFS volumes can also be expanded using LUN expansion. Add or delete an ESXi server from a VMware VMFS volume without disrupting other ESXi servers. file name change, file size change, etc.) SCSI reservations are only implemented when logical unit number (LUN) metadata is updated (e.g. Allows access by multiple ESXi servers at the same time by implementing per-file locking. Optimization include aggressive caching with for the DAS use case, a stripped lock down lock manager and faster formats. Leaf level VSAN objects reside directly on VMFS-L volumes that are composed from server side direct attached storage (DAS). VMFS-L is the underlying file system for VSAN-1.0. It supports 512 emulation (512e) mode drives. Notably, it raises the extent limit to 64 TB and the file size limit to 62 TB, though vSphere versions earlier than 5.5 are limited to VMDKs smaller than 2 TB. Notably, it introduces directory structure in the filesystem. VMFS3 is used by ESX Server v3.x and vSphere 4.x. VMFS2 is a flat filesystem with no directory structure. VMFS2 is used by ESX Server v2.x and (in a limited capacity) v3.x. VMFS1 is a flat filesystem with no directory structure. It did not feature the cluster filesystem properties and was used only by a single server at a time. VMFS0 can be reported by ESX Server v6.5 as a VMFS version when a datastore is unmounted from a cluster/host. Conversion to GPT happens only after you expand the datastore to a size larger than 2 TB.There are six (plus one for vSAN) versions of VMFS, corresponding with ESX/ESXi Server product releases. If your VMFS5 datastore has been previously upgraded from VMFS3, it continues to use the master boot record (MBR) partition format, which is characteristic for VMFS3. The GPT format enables you to create datastores larger than 2 TB. Any new VMFS5 or VMFS6 datastore uses GUID partition table (GPT) to format the storage device. Do not mix devices of different formats within the same datastore cluster. However, all datastores in the cluster must use homogeneous storage devices. VMFS5 and VMFS6 can coexist in the same datastore cluster. vCenter Server performs compatibility checks to validate Storage vMotion across different types of datastores. Storage vMotion supports migration across VMFS, vSAN, and Virtual Volumes datastores. VMFS5 and VMFS6 datastores support the block size of 1 MB. 
The block size on a VMFS datastore defines the maximum file size and the amount of space a file occupies. The spanned datastore cannot extend over devices of different formats. A spanned VMFS datastore must use only homogeneous storage devices, either 512n, 512e, or 4Kn. When you work with VMFS datastores, consider the following: Storage vMotion across different datastore types SEsparse for virtual disks larger than 2 TB. VMFSsparse for virtual disks smaller than 2 TB. Support for virtual machines with large capacity virtual disks, or disks greater than 2 TBĭefault use of ATS-only locking mechanisms on storage devices that support ATS.
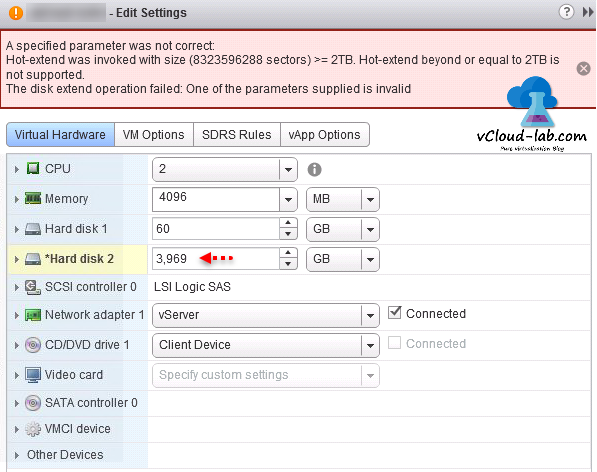
Storage devices greater than 2 TB for each VMFS extent See Manually Reclaim Accumulated Storage Space.įor a VMFS5 datastore that has been previously upgraded from VMFS3.
#Vmware vsphere 6.5 vmdk file size limit manual
Manual space reclamation through the esxcli command. Comparing VMFS5 and VMFS6 Features and FunctionalitiesĪccess for ESXi hosts version 6.5 and laterĪccess for ESXi hosts version 6.0 and earlier The following table compares major characteristics of VMFS5 and VMFS6.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
